Choose Language
September 29, 2022
NewsA plummeting pound complicates matters for the Bank of England
Globally, central banks are walking a very thin tightrope, attempting to contain soaring inflation without sending their respective economies into a tailspin. Nowhere does this look more precarious than in the UK, with the task complicated by the new government’s planned tax cuts and a plummeting pound.
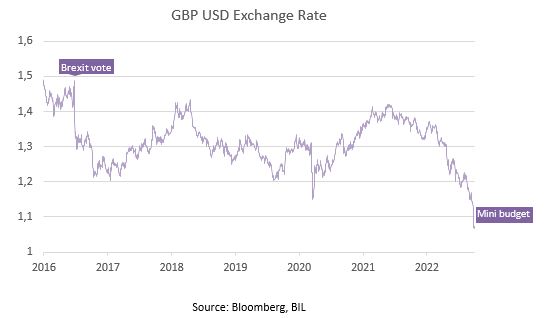

While sterling had already been weakening against the US dollar over the past year, the unveiling of Chancellor Kwasi Kwarteng’s “mini budget” on September 23 was the clincher, sending the exchange rate to a record low.
The budget delivered a broad swathe of debt-funded tax cuts aimed at boosting growth and energising the economy. In reality, the cuts amounting to £45bn were perceived as potentially working at cross purposes to monetary policy, even by the IMF which urged the government to “re-evaluate” the plan, warning that the “untargeted” package might stoke inflation further.
As such, the economic plan put a huge dent in investor confidence, with some doubting whether the government would be able to fund these cuts against a backdrop of higher borrowing costs and ailing growth. The decline in confidence was visible not only sterling’s decline, but also in a rout in the UK government bond market, so severe the BoE had to step in to stave off a crash by pledging unlimited purchases of long-dated bonds and postponing quantitative tightening until October 31st (previously Oct. 3rd).
The BoE has been trying to orchestrate the softest possible landing for the economy as it attempts to cool inflation (which came in at 9.9% in August). This is a highly delicate task at the best of times, usually ending in recession (the BoE has said the UK might already be in one). Today, it is further complicated by the ongoing energy crunch in Europe, elevated utility bills and residual supply chain problems. While other central banks like the ECB have said that they will fine-tune their policy decisions with incoming data moving forward, the BoE has probably now been shoe-horned into hiking by even more than it would have initially to control the situation, increasing the chances of a deeper economic downturn.
The primary reason is that the plummeting pound is inflationary in itself, especially given that Britain imports about half of the goods it consumes. Following the announcement, BoE Chief Economist Pill said that “this will require a significant monetary policy response”, leading investors to price in a terminal rate above 6% next year; the current rate is 2.25%.
By hiking rates, the BoE can rein in demand and ultimately prices. By its own estimates, a 2 percentage point rise in interest rates could reduce aggregate spending by 1%. Higher rates would likely also take a toll on British manufacturing through higher input costs and exacerbate the cost of living crisis (by pushing up mortgage rates and debt servicing costs). This is of course not ideal for the UK economy but failing to act on inflation now could lead to even more severe consequences further down the line. So of course, the ultimate goal is to contain inflation with as few hikes as possible.
What the Bank of England cannot do is single-handedly entice foreign investors back into sterling and UK government bonds. Absent a U turn or at least some concessions from the Treasury on the budget, the BoE will probably continue to fight an uphill battle to decrease inflation, with a weak pound pushing against its efforts.
Analysts now expect a 100bp rate hike on Nov. 3, with risks skewed to a larger, earlier move.
For governments around the world, the lesson is clear: coordinated fiscal and monetary policy will be essential if we are to get inflation back under wraps.
More
July 18, 2024
BilboardBILBoard August 2024 – Stocks get tha...
Based on the Committee of 15th July 2024 Over the past few weeks, two important developments have played out for investors. Firstly, US inflation...
July 16, 2024
NewsTourism, a fragile pillar of Europe&#...
Accounting for around 10% of the EU's GDP, tourism is one of the key pillars of the European economy, with a considerable impact on...
July 1, 2024
NewsCan US households continue driving gr...
Consumers are the Atlas holding up the American economy. With the US representing around one-quarter of global output, and with personal consumption accounting for an...
June 21, 2024
BilboardBILBoard – Summer 2024
Despite tight monetary conditions, the global economy held up remarkably well throughout the first half of 2024. From this point on, it appears to be...

